Learning from the Earthworks
Thickness Meets Temperature
How Does Climate Become Architecture?
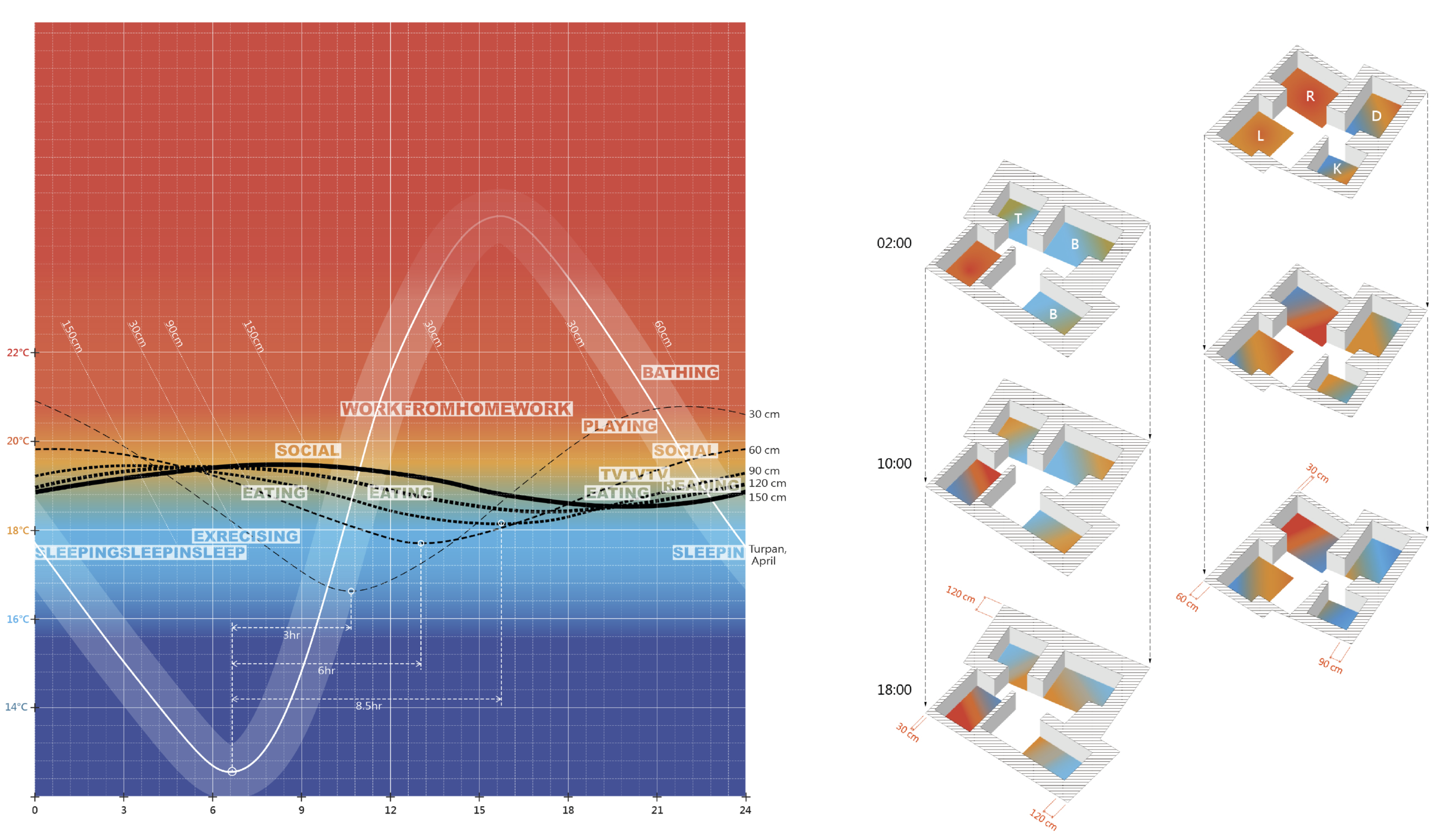
In modern construction logic's pursuit of building performance, tactile experience and microclimate perception of the human body are often overlooked. This project reexamines the embodied wisdom in traditional rammed earth architecture, studying how it creates rich tactile experiences and comfortable microclimates through material properties and constructional details. Taking Turpan region as the site, through precise analysis of temperaturetime curves and integration of modern prefabrication technology with traditional methods, the project develops a new type of sustainable architecture that responds to human sensory needs at different scales. From the tactile properties of materials to the regulation of spatial microclimates, it reestablishes the direct connection between architecture and the user's body.

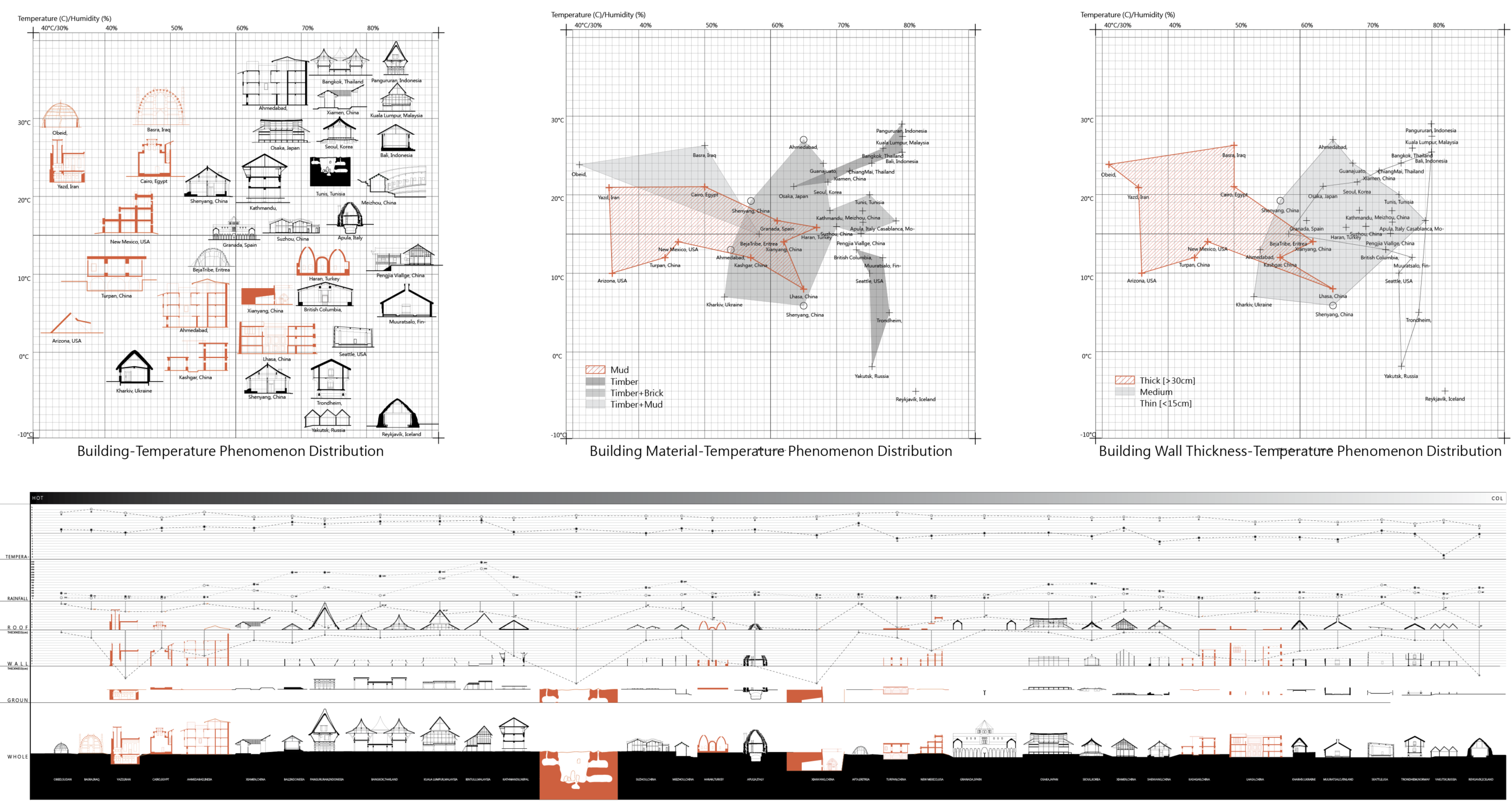
Index of Global Climate and Vernacular Architecture
This studio begins with the relationship between climate and architectural typologies. It identifies representative traditional architectural samples from global climatic typologies and categorizes them based on the distribution of building forms, materials, and climatic conditions such as temperature and humidity. This project focuses on thick walls as a point of entry, further investigating the scale of thick-wall architecture, materials, and their adaptation to climate change.
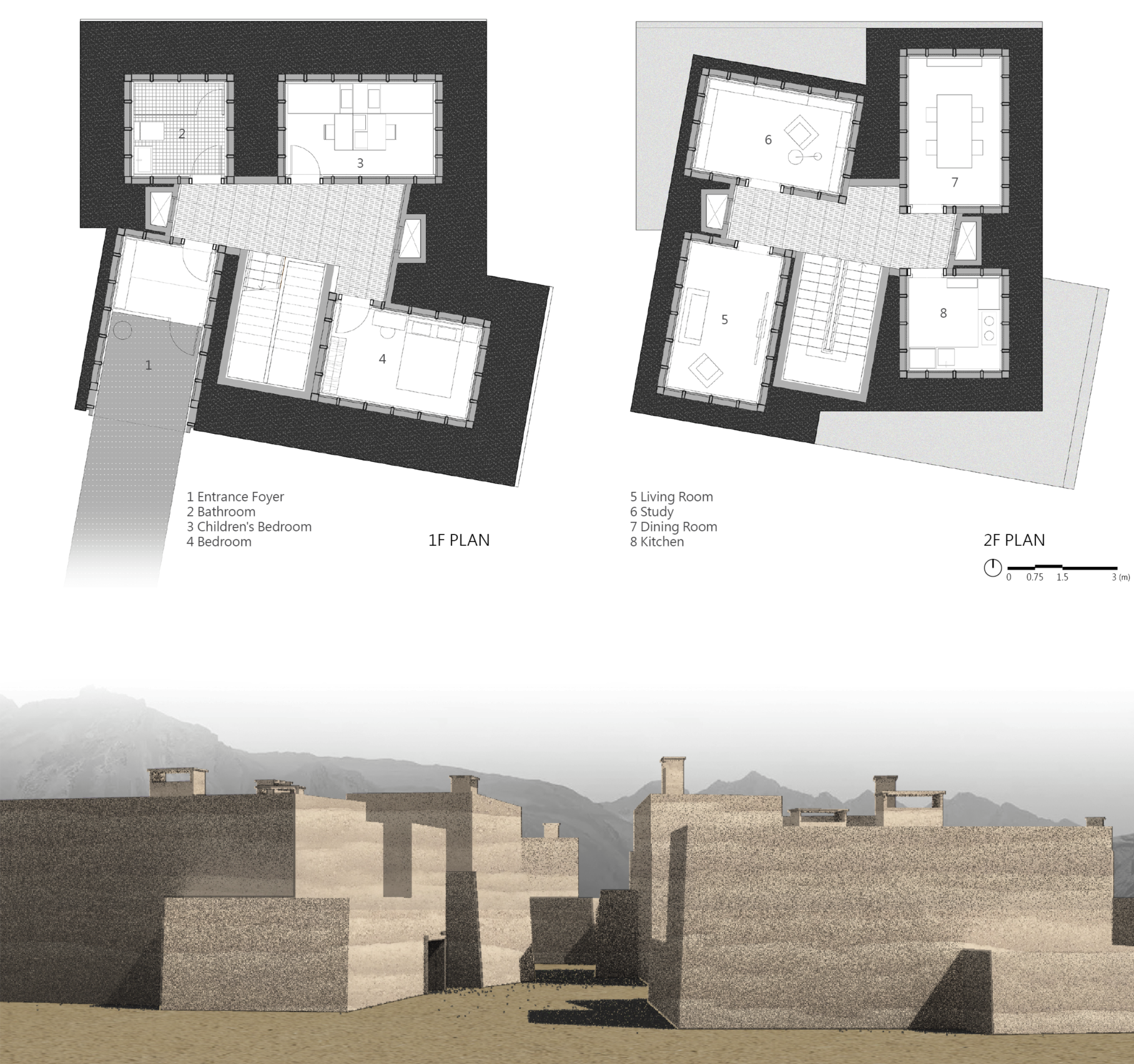
Traditional / Modern Approach
Rammed earth architecture embodies ecological, corporeal, and cultural symbolism, shaping organic traditional settlements; modern architecture is characterized by high productivity, efficiency, and dense planning. The intersection of these two forms represents a sustainable path for the future of architecture and urban development.

Tectonic of Rammed Earth Architecture
From a technical perspective, earth has a high specific heat capacity, enabling passive thermal regulation to control indoor temperatures. Once compacted and air-dried, rammed earth also offers structural stability and weather resistance. On a cultural level, earthworks provide tactile experiences through material texture, as well as temperature and humidity sensations.
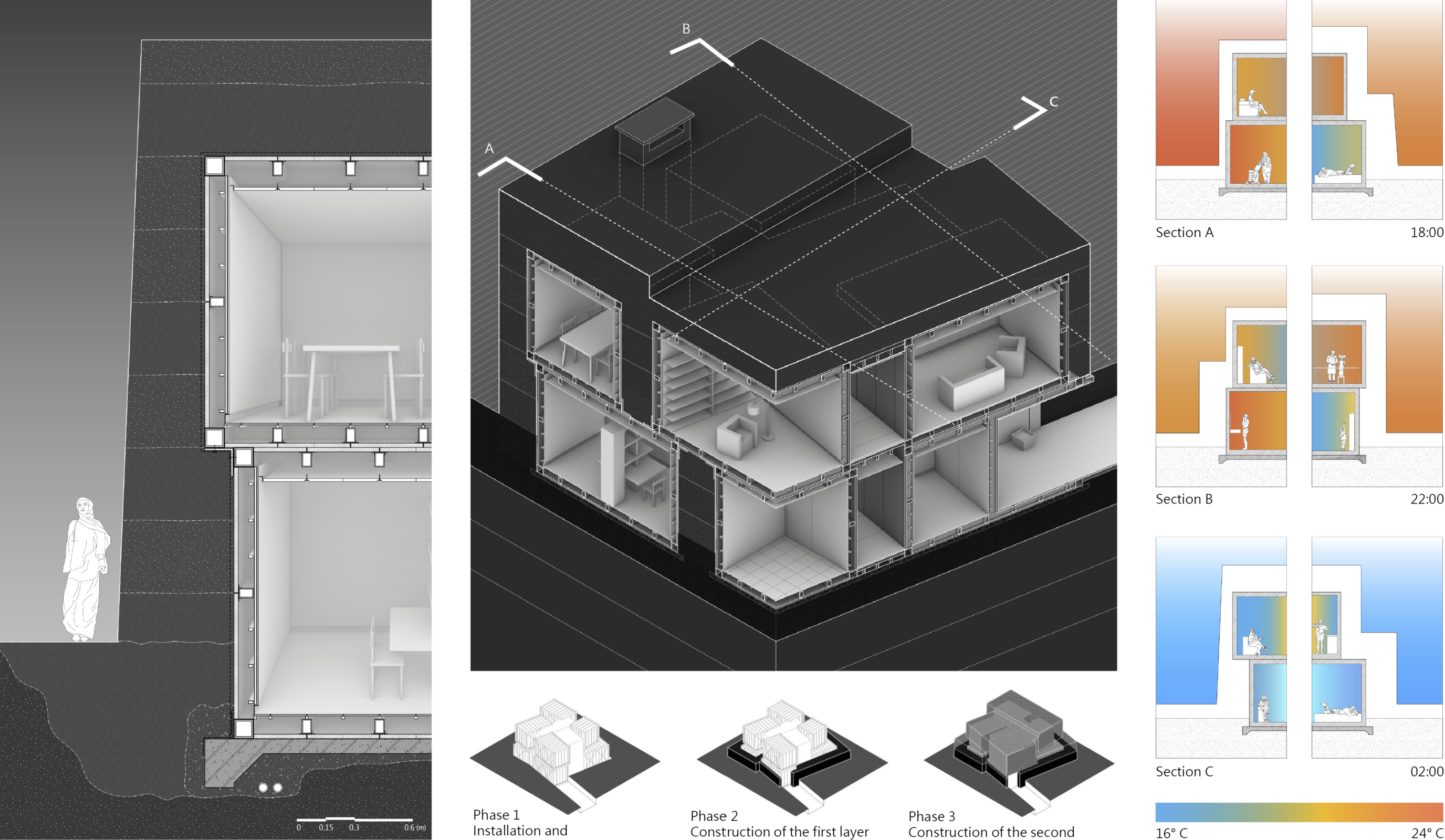
A Tectonic Fusing Tradition and Modernity
Traditional rammed earth naturally regulates temperature, while modern precast modules enhance stability and streamline construction. Serving as inner molds, these units shape varied wall thicknesses via their recessed and protruding surfaces, enabling large, smooth outer formwork. The method merges structural strength, efficiency, material performance, and cultural symbolism, creating a new tectonic expression that bridges tradition and modernity.